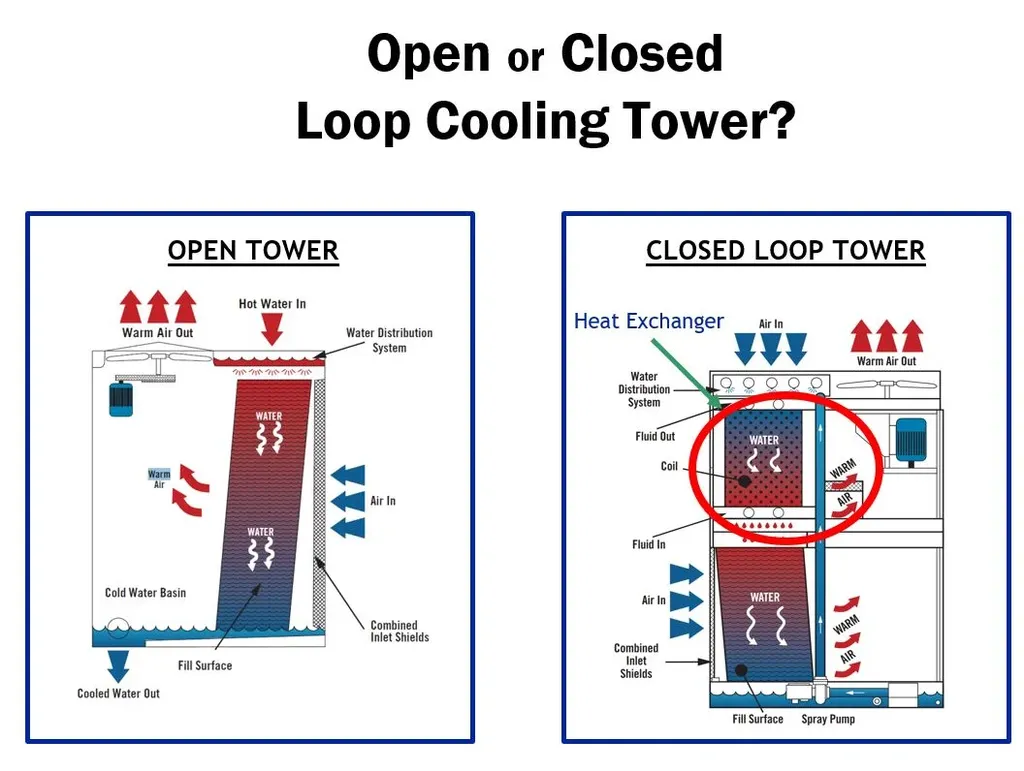
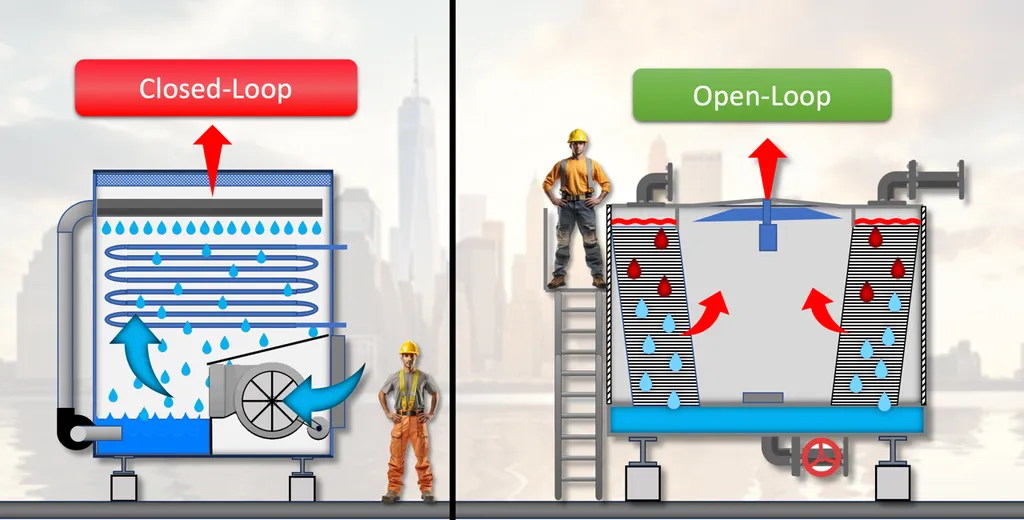
Kaltra, an international company headquartered in Munich, stands at the forefront of innovation in cooling technology. They craft energy-efficient chillers, free cooling systems, precision air conditioners, and microchannel heat exchangers tailored for data centers and various industries. Operating in over 60 countries, Kaltra prioritizes environmental friendliness and unwavering reliability. But what makes their technology so compelling? A significant portion of their success resides in the ongoing debate between two fundamental heat exchanger designs microchannel and tube.
Understanding the Players, Microchannel and Tube Heat Exchangers
Before we dive into the comparison, it’s crucial to understand what each technology brings to the table. Tube heat exchangers, a more established technology, utilize a network of tubes to circulate the refrigerant. Air flows over these tubes, facilitating heat exchange. They’re known for their robust design, relatively simple manufacturing process, and tolerance for less-than-ideal water quality.
Microchannel heat exchangers, on the other hand, represent a more modern approach. They consist of flat tubes containing multiple parallel microchannels. These tiny channels significantly increase the surface area available for heat transfer. What does this increased surface area translate to? Greater efficiency and a more compact design.
The Battle for Efficiency, Where Does the Advantage Lie?
The core of the debate often boils down to efficiency. Which design extracts heat more effectively? Microchannel heat exchangers generally boast superior heat transfer coefficients compared to their tube counterparts. The increased surface area allows for more efficient heat exchange, leading to better overall system performance. This translates to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs, especially important in demanding environments like data centers.
However, tube heat exchangers have their own strengths. Their simpler design often means lower initial manufacturing costs. Furthermore, they’re often more forgiving of fouling, where deposits build up on the heat transfer surfaces. In applications with poor water quality, this robustness can be a significant advantage.
The Space Race, Compactness and Design Flexibility
In today’s world, space is a premium. How do microchannel and tube heat exchangers stack up when it comes to size and design flexibility? Microchannel technology generally offers a more compact footprint. The efficient design allows for smaller units that deliver the same cooling capacity as larger tube-based systems. This is particularly beneficial in situations where space is limited, such as retrofitting existing facilities or designing high-density cooling solutions.
Tube heat exchangers, while typically larger, can be more easily customized to fit specific application requirements. Their design allows for greater flexibility in terms of shape, size, and material selection. This adaptability can be crucial in niche applications where standard solutions won’t suffice.
Durability and Maintenance, Long-Term Considerations
Beyond immediate performance, the long-term durability and maintenance requirements of each technology are crucial. Tube heat exchangers, with their robust construction, are generally known for their long lifespan. They can withstand harsh operating conditions and are relatively easy to repair.
Microchannel heat exchangers, while highly efficient, can be more susceptible to fouling and corrosion. The tiny channels can be easily blocked by debris, reducing performance and potentially leading to failure. However, advancements in materials and manufacturing processes are constantly improving their durability and resistance to corrosion. Choosing the right fluid treatment and implementing a proper maintenance schedule are essential to ensure the longevity of microchannel systems.
The Economic Equation, Weighing Costs and Benefits
Ultimately, the choice between microchannel versus tube heat exchangers hinges on a careful economic evaluation. While microchannel systems may have a higher initial cost, their superior efficiency can lead to significant savings in energy consumption over the long term. Tube heat exchangers, on the other hand, offer a lower upfront investment but may result in higher operating costs.
Factors such as the application’s energy requirements, operating conditions, maintenance costs, and expected lifespan must be considered to determine the most cost-effective solution. A thorough lifecycle cost analysis is crucial to making an informed decision.
Kaltra’s Perspective, Innovation and Environmental Responsibility
Kaltra’s commitment to environmental friendliness and reliability drives them to continually innovate in cooling technology. They offer a range of solutions incorporating both microchannel and tube heat exchangers, tailoring their designs to meet the specific needs of their clients. Whether it’s maximizing energy efficiency in a data center or providing robust cooling for an industrial application, Kaltra strives to deliver solutions that are both environmentally responsible and economically sound. The ongoing evolution of microchannel versus tube technologies continues to shape the future of cooling, and Kaltra remains dedicated to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As the debate around microchannel and tube designs evolves, Kaltra helps their clients navigate these choices with data-driven insights.